Earth is surely the most beautiful and complex planet of the Solar system; Beautiful for its landscape, and complex for its composition. The various elements, of which Earth is composed, have made it habitable and have been supporting the origin, growth and survival of all living beings. The natural resources present on Earth, have enabled humans to create and produce things for making their lives easier, and more comfortable. Since its origin, the human race has come a long way; from caves to skyscrapers; from being gatherers to mass producers; from stone tools to nuclear reactors; from walking miles to flying; from struggling for survival to ruling the planet; humans have transformed everything around them, and the driving force behind this transformation is “energy”. The universe we live in, stores tremendous amount of energy within itself; the Sun, our planet and its various components are capable of producing energy and humans have been able to identify some of these sources and harness energy in various forms. Our conventional method of producing energy requires burning of fossil fuels; this has adversely affected our environment by causing pollution, and also by over exploitation of natural resources. The disadvantages of extracting energy from conventional sources surpass its advantages, as energy sector is responsible for nearly 60% of total carbon emissions; therefore, the demand of generating green and clean energy is growing rapidly. Despite a sharp rise in production of renewable energy, 3 billion people still rely on wood, coal, charcoal, and animal waste for cooking and heating, leading to indoor air pollution which causes millions of deaths each year. Modern living depends heavily on electricity, yet 13 per cent of global population still lacks access to modern electricity. Realizing the need of availability of sustainable electricity, SDG 7 – Affordable and Clean energy was launched by the United Nations in the year 2015, as part of its agenda 2030. SDG7 aims to ensure access to affordable, reliable and sustainable electricity, worldwide.
Renewable energy in India
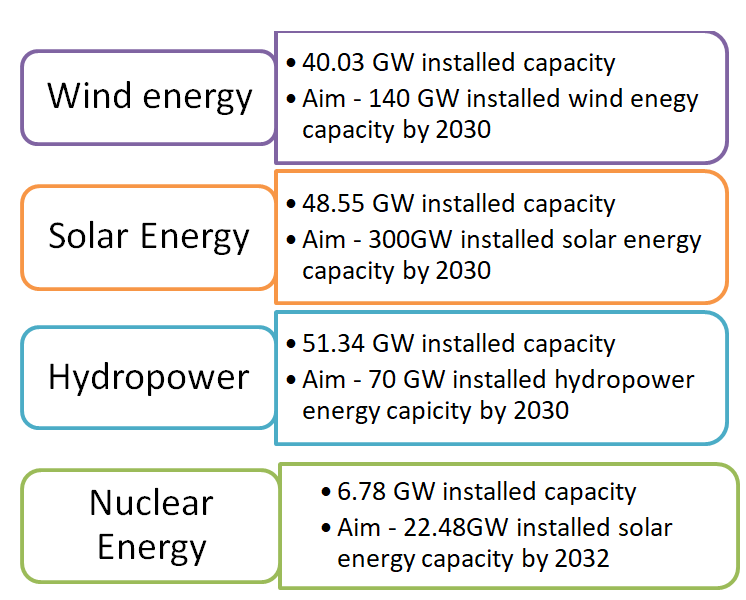
India is one of the leading nations, in terms of producing renewable energy. India’s present installed electricity generation capacity from non-fossil sources is 157.32GW, which is 40.1% of its total installed capacity, and is much ahead of meeting its committed target of achieving 40% of its electricity generation from fossil fuels by 2030, in the Paris Agreement. India now aims for achieving 50% of its total electricity capacity from renewable sources, by 2030 as Prime Minister Narendra Modi announced to have 500GW non-fossil fuel energy capacity in India
Major renewable energy sources in India and their capacities.
Role of business
Apart from these major renewable energy sources, the world is looking forward to adopting new technology for generating clean energy to fulfil its ever rising demand of energy, while conserving nature. There is also an urgent need to generate employment and business opportunities to help our economy recover the damage caused by the global pandemic. Scientists all around the world are involved in research and development activities for producing clean energy and increasing energy efficiency for the implementation of SDG7 and supporting both the environment, and the economy. Business can play an important role in achieving SDG7 by providing financial support and adopting new technologies for producing and conserving energy, as industries are responsible for about 50% of global power consumption. Improving energy efficiency is as important as consuming renewable energy, and industries need to incorporate both these practices throughout their supply chains and value chains for effective implementation of SDG7. Using electricity efficiently can save energy cost to a great extent while innovation in energy sector can open new markets and create new business opportunities.
Business Ideas supporting SDG7
Generating energy from Industrial waste
Waste management is a major concern for all industries. So far, people have been working on providing safe and eco-friendly solutions for disposal of industrial waste, but in recent years, people have come up with innovative ideas for managing waste in a productive and profitable way. Generating electricity from industrial waste is an emerging trend and many institutions are already involved in research and development programmes for facilitating the same. As per studies, industrial waste can be used to generate power, in all its forms; solid waste, waste water and waste gases.

Biogas power plant
Biogas has been widely accepted in India as a household fuel, especially in rural areas. it is majorly used for cooking, but it is now being considered as a fuel for generating electricity. Bio gas power plants are based on the process of biodegradation of cow dung and other bio-waste, and are therefore highly cost-efficient and eco-friendly. Recently, Haryana’s first grid-connected 1.2 MW bio-gas based power plants have been commissioned. Such plants are well supported by government policies and would prove to be a promising business plan in near future.
Geothermal energy
Geothermal power plants are popular renewable energy establishments in USA and many European countries. These plants make use of the heat that comes from the sub surface of Earth, to generate electricity. Deep wells are dug to access the hot water present under rocks and use it to drive turbines. Many sites in India are being tested for geothermal energy, and the country’s first geothermal power plant has been set up in Gujarat’s Dholera, where immense heat was found under the Earth in the form of hot springs. The plant would produce 20 KW of electricity. India has the potential to produce much higher amount of electricity through geothermal power plants, and add to its economic development.
Tidal energy
The tides of Seas and Oceans carry tremendous energy; this energy can be harnessed and converted into electricity by installing power generation set-up at suitable sites. Presently, there are very few tidal power plants around the world, but tidal power has the potential to become a major source of renewable energy. As per studies, India has an estimated potential of producing 12.5 GW of tidal power, spread across coastlines of Gujarat, Tamil Nadu and West Bengal. Presently India’s Tidal Power projects have been shelved due to financial constraints, but with proper planning and better investments, Tidal power could be used in India for producing clean and green energy.
Marine algae as biofuel
Studies are being conducted all around the world, to derive techniques for commercial use of Marine algae as biofuel. The potential of marine algae is well known to scientist and researchers working on biofuel sources. Marine algae are considered superior to terrestrial plants in terms of storing solar energy and carbon. They also have higher photosynthetic efficiency and higher biomass yield. Marine algae are expected to play an important role as biofuel for producing energy in future.
Green energy entrepreneur
Various types of power plants for producing electricity are definitely large scale projects. But, this does not mean, green energy business is not meant for small entrepreneurs. Entrepreneurs too have great prospects in implementing green energy solutions at small scale. There are various products and services associated with generation, storage, conservation and distribution of energy, providing innumerable innovative business opportunities for entrepreneurs. Through research, training and planning, anybody can become a green energy entrepreneur or a green energy investor, and contribute to the Nation’s sustainable development.

