We all are familiar with the term Infrastructure, which refers to the basic physical systems that are required for smooth functioning of an Industry, city, state or nation, and we are also aware of the importance of these systems in the path of development. but, when we talk about sustainable development, we need to think beyond these man-made infrastructure systems. Though these systems make our lives and movement convenient and have become an integral part of our survival, they have some negative impacts on our environment too. The negative impacts of infrastructure development include;
- Overuse of natural resources
People having easy access to water, especially in urban areas, tend to overuse and even waste large quantities of fresh water.
- Air, water and noise pollution
Construction of various components of infrastructure, like buildings, roads bridges, dams etc. cause air, water and noise pollution through the process of construction.
- Depletion of natural resources
Many trees are cut down to provide land for infrastructure development , resulting in deforestation, which further leads to soil erosion.
- Disturbed ecosystems
Construction activities, industrial development and mining activities destroy and disturb the natural habitat of many plant and animal species, which leads to the loss of biodiversity. Many species are being driven to extinction and many other have become endangered.

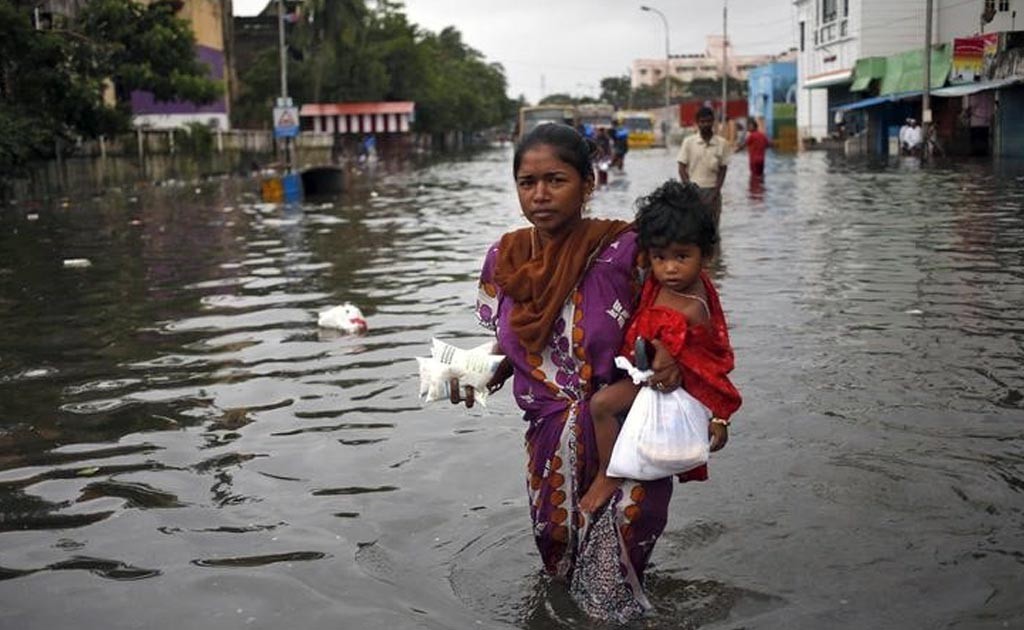
Infrastructure development over decades has affected our environment badly and is adding to the problem of climate-change. These disturbances later result in natural disasters like floods, wildfires, and earthquakes etc., which are on a rise since past few decades. There is an urgent need to minimize the negative impacts of infrastructure development and make it more resilient. If Natural elements are added to man-made infrastructure systems, many environmental issues can be resolved, disaster risks can be minimized, resources can be conserved, and both nature and humanity can be benefited. These solutions have inspired the formulation of the concept of “Natural Infrastructure.

An Infrastructure where natural systems are planned and managed along with man-made systems for sustainability of cities and communities, is usually regarded as natural infrastructure. Natural infrastructure provides low-cost and eco-friendly services which are essential for maintaining the quality of life of people living in a city or community. including natural infrastructure in town planning strategies , is an effective way to deal with major issues faced by people living in both rural and urban areas, like water shortage, storm water management, wastewater treatment, poor air-quality etc. let us try to understand how natural infrastructure brings about sustainability through some examples;
- Preamble pavements and driveways

Permeable pavements and driveways are made of highly porous concrete, which allows rainwater or storm water to pass through and flow it down to underground aquifers. This is a low-cost and effective way to manage storm water, prevent flood and recharge ground water.
- Wetlands
Wetland is an area ,where soil is covered with water. Constructed wetlands contain soil, vegetation, bacteria etc., which breakdown and remove pollutants and nutrients naturally from wastewater and treat water naturally. Such systems are highly cost effective and environment friendly. They store good amount of carbon and support biodiversity.
- Green roofs and vertical gardens

Planting gardens on roofs and along walls (vertical garden) has become a popular trend, especially in urban areas where there is lack of land for planting gardens. These gardens add to the aesthetic value of a place and reduce air and noise pollution. These gardens absorb carbon and other pollutants and improve air quality. They help reduce temperature –rise due to urban heating These gardens also prevent storm water runoff.
- Mangrove restoration

Mangroves are found in coastal areas and have many benefits including environmental and economical benefits for people living in coastal areas. They provide ideal habitat for many land and water species, which is highly beneficial for local fishermen. They act as natural barriers against disasters like floods and absorb carbon.
Economical benefits of natural infrastructure
With only a decade left to meet the targets of sustainable development gaols and to make up for the economic losses due to COVID-19, people are now looking for new business ideas and employment opportunities based on sustainability. building natural infrastructure , can be helpful in creating employment opportunities and generating income with very little investments.
SDGs and natural infrastructure
With proper planning and implementation, Natural infrastructure can help meet the targets of many SDGs, but the SDG that is very closely related to Natural infrastructure is SDG 11.
SDG 11- Sustainable Cities and Communities
- By 2030, ensure access for all to adequate, safe and affordable housing and basic services and upgrade slums
- By 2030, significantly reduce the number of deaths and the number of people affected and substantially decrease the direct economic losses relative to global gross domestic product caused by disasters, including water-related disasters, with a focus on protecting the poor and people in vulnerable situations
- By 2030, reduce the adverse per capita environmental impact of cities, including by paying special attention to air quality and municipal and other waste management
- By 2030, provide universal access to safe, inclusive and accessible, green and public spaces, in particular for women and children, older persons and persons with disabilities
- Support positive economic, social and environmental links between urban, peri-urban and rural areas by strengthening national and regional development planning
- By 2020, substantially increase the number of cities and human settlements adopting and implementing integrated policies and plans towards inclusion, resource efficiency, mitigation and adaptation to climate change, resilience to disasters, and develop and implement, in line with the Sendai Framework for Disaster Risk Reduction 2015-2030, holistic disaster risk management at all levels
Public sector, private sector and government need to collaborate and include natural infrastructure in their sustainability strategy. The numerous benefits of natural infrastructure would help people live better lives and build sustainable cities for future generations.